Recruitment, Selection and Induction | Understanding Talent Acquisition

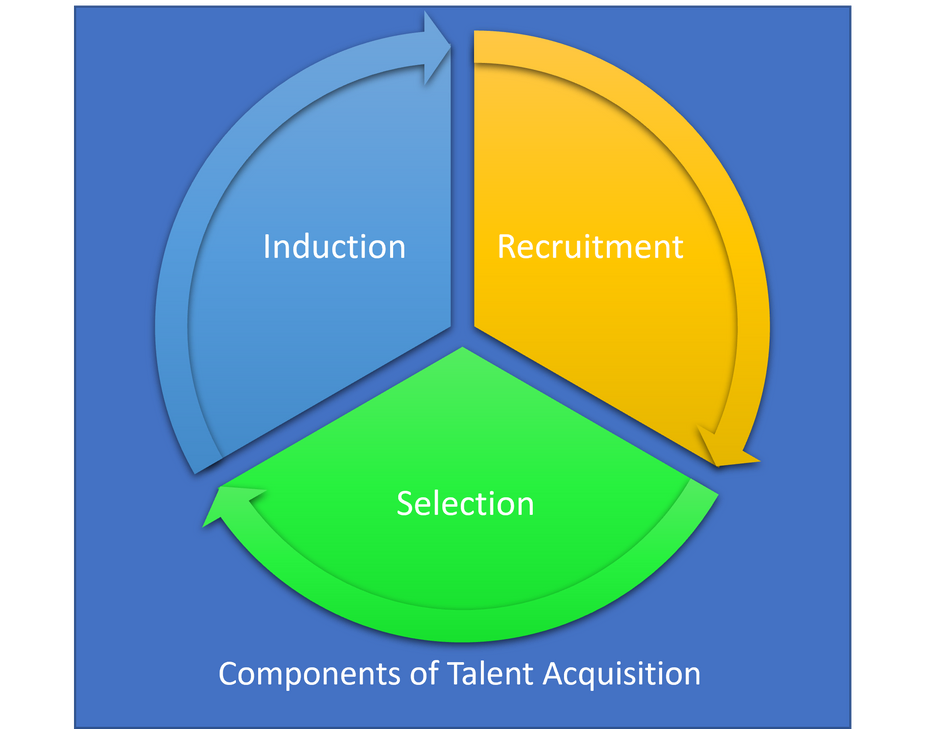
In order to ensure on demand availability of talent pool in an organization, both qualitatively and quantitatively, recruitment, selection and induction are important and ongoing process in the HR department. Modern HR has come a long way from the days of personnel management. Strategic human resources as it in frequently referred to, is proactive rather than being reactive. By making the resources available to the functional departments as per their quality and quantity requirements, HR department makes its own contribution to the overall corporate strategy. Let us study these components of talent acquisition in more detail in this chapter.
Talent Acquisition
Recruitment, selection and induction are consecutive and interlinked processes in HRM that aim to ensure availability of human resources to meet the strategic needs of an organization. It may be noted that recruitment is an accumulative process and selection is an eliminative process. Induction on the other hand is an onboarding process to ensure that the employee and the organization settle down with each other as quickly and as positively as possible to ensure that the employee becomes productive at the earliest.
Recruitment
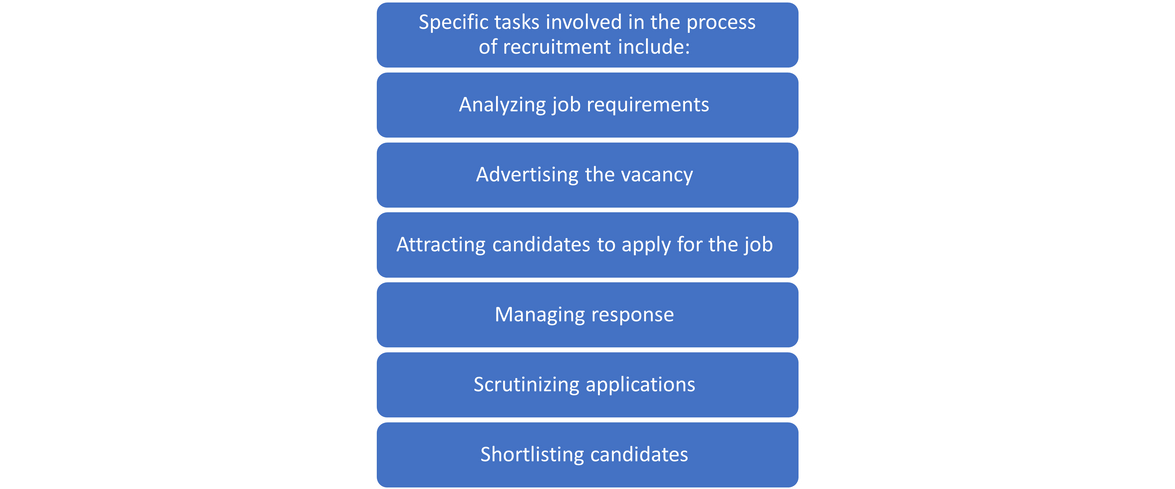
The process of identifying the right talent externally or even internally as per the job analysis done earlier. The identified talent is screened and presented for selection. It involves the following steps;
- Identifying the job openings in the organization
- Identifying talent, externally or internally matching the job specifications
- Attracting applications from suitable talent
- Screening applicants to shortlist best suited candidates
- Presenting the candidates for further selection process
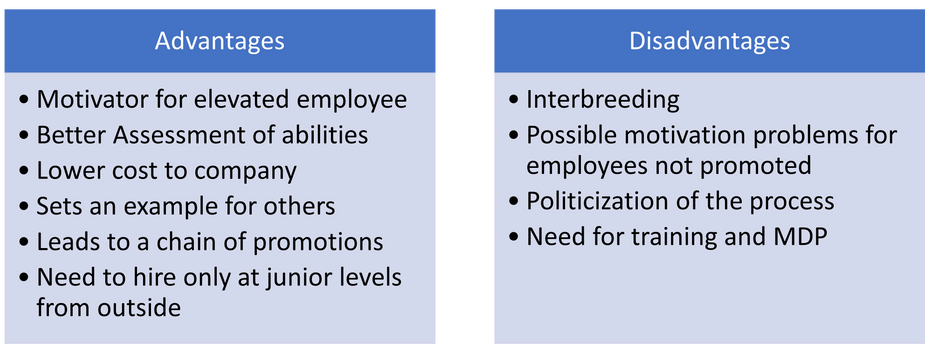
Sources of Recruitment (Internal)
- Internal Job Postings (IJP) – IJPs are posted across internal forums in the organization. IJPs are a good source of attracting internal talent for recruitment.
- Promotions & Transfers – Promotions and transfers planned and executed to realign the existing talent with the changing work requirements.
- Buddy Referrals – Instead of paying outside placement agencies, organizations offer incentives to existing employees to recommend their friend from their own professional network. This is a win-win situation, both for the company and the referring employees.
- Re-hiring former employees – Rehiring former employees without any grudges or prejudices is a good idea. This strategy saves a lot of cost and time in bringing an employee up to productive level.
Sources of Recruitment (External)
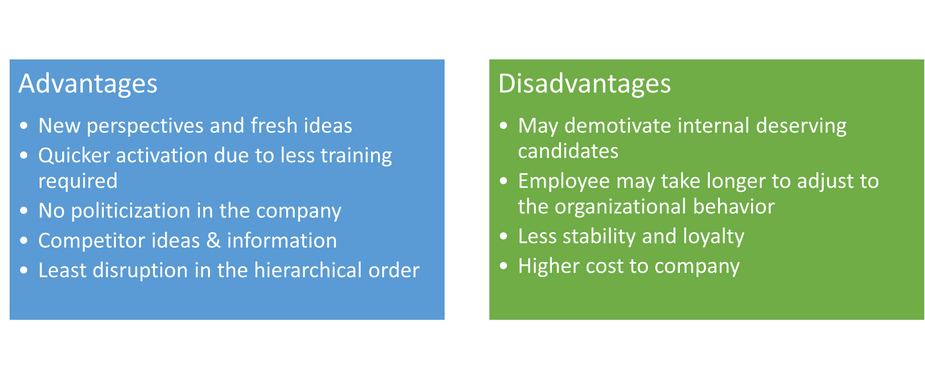
- Educational/Training Institutions – Campus recruitments as they are popularly known are a good sources of hiring freshers with a very clear lineage.
- Employment Agencies – Employment agencies maintain a database of employees who are looking for a job change. They provide ready source of recruitment, but of course at a cost.
- Employment Portals – Employment portals are like the matrimonial sites of the corporate world. Both job seekers and talent seekers post their requirements and the match making happens online.
- Social Media – Almost all social media platforms also do have jobs page as well. Recruiters keep scouring these pages to catch good fish.
- Conventional Media – Conventional media such as newspapers are still a good source of recruitment, especially in conventional industries such as manufacturing.
- Professional Networking – Recruiters maintain their own database and networking as their personal intellectual property. They use this to recruit candidates for whichever company they are hired to do the job.
Factors Affecting Recruitment (Internal)
- Remuneration – The general levels of remuneration a company offers as compared to the industry standards either make it a preferred employer or a deferred employer thus impacting the recruitment response from the market.
- Nature of Work – The peculiarity or the generality of the work for which the recruitment is being done also impacts the amount of applications received.
- Organizational Culture – How happy an organization keeps its employees is no secret in the market and largely influences that interest potential candidates show in its recruitment drives.
- Career Options – What career options a company has to offer in the near, middle and far future impacts the decision to apply for its advertised openings.
- Company Size & Image – Overall corporate image and the stability of a company are important factors that candidates evaluate before considering to apply for an opening there.
- Company’s Growth – Company’s performance and future plans are important to career minded candidates who look at the long term prospects of staying in the organization.
- Cost Of Recruitment – The cost of recruitment is an important component that impacts the recruitment process. The typical costs in recruitment process are the incentives paid to employees for buddy reference or commissions paid to external vendors for sending in applications. In any case, the overall cost of recruitment will influence the quantity and quality of applications received.
Factors Affecting Recruitment (External)
- Socio-Economic Factors – The socio-economic factors such as the composition of the families, the proportion of country’s population living in urban areas versus rural areas, the availability of women in the workplace, and the general age at which people start working and stop working, all of them impact recruitment for any company operating in that society.
- Supply & Demand Factors – The availability of candidates and the demand created by companies have to be in a balance. If this balance is disturbed, say for example, the availability of the workforce is much less as compared to the requirement requirements, then all the recruiters will be under a lot of pressure and on the other hand if the availability of the candidates is high, then recruitment becomes an easy job.
- Employment Rate – The employment rate of a particular region will impact recruitment. If the employment is high, the candidates will be already employed with some or the other organization. In such a scenario recruitment becomes challenging and on the other hand if the employment rate is low, there will be lot of people looking for a job which makes recruiting an easy job.
- Labor Market Condition – Labor market conditions such as labor regulations, the presence of industrial unions, recruiting norms set by the government etc. will impact recruitment deeply.
- Reservation System – If the government of a country provides reservations to certain sections of the society, then it is mandatory for companies to comply and carry out their recruitment in accordance with those reservation systems. This impacts recruitment because unless the candidates who come from reserved categories are offered jobs, general category candidates cannot be invited to apply.
- Market Competition – If there are a lot of companies operating in the market having similar requirement of candidates, this leads to a shortage of desired manpower, thus putting a lot of pressure on recruitment and leaving them with fewer choices.
- Information System – How well a society is connected in terms of its communication channels, infrastructure, interaction, and sharing of information will determine the speed & ease of recruitment by influencing the exposure of advertised vacancies over a larger population. The same information technology will also facilitate the application process.
Also Read – Human Resources Management, An Introduction
Selection
Selection is the process of identifying an individual from a pool of job applicants created earlier during recruitment with the requisite qualifications and competencies to fill jobs in the organization. This is an HR process that helps differentiate between qualified and unqualified applicants by applying various techniques. The term ‘selection’ comes with the connotation of placing the right person in the right job. Selection is the process in which various strategies are employed to help recruiters decide which applicant is best suited for the job.
Selection Criteria
The selection process is a largely time-consuming step in an employee’s hiring experience. HR managers must carefully identify the eligibility of every candidate for the post by carefully evaluating the following KSA criteria;
•Formal Education
•Experience & Past Performance
•Physical Characteristics
•Personality Characterizes
Selection Process
Selectors employ multiple steps to identify right candidates, some of which are discussed below;
Screening – This is a redundant step because mostly the screening of the candidates and their resumes have already been done during recruitment phase. However, still selectors may want to further weed out any unsuitable candidates that may have passed the recruitment stage. Typical screening methods include;
- Telephonic Interviews
- Group Discussions
- Case Solving
- Pre-selection Assignment
Testing – Testing methods are employed to evaluate the suitability of the candidates w.r.t. to their knowledge, personality and psychology. Some of the common types of tests that the candidates are put through are as follows;
- Cognitive Ability Testing – To test the reasoning, thinking and information processing abilities of a candidate.
- Physical Ability Testing – To check the physical abilities of a person to be able to meet the demands of some jobs like those in the armed forces, manufacturing companies, law enforcement, and fashion & glamor industries.
- Personality Testing – There are many aspects of candidates’ personality that might require evaluation such as the degree of introversion, ability to work in teams and leadership qualities, based on the requirements of the job in question.
- Integrity Testing – Most companies while selecting candidates for any position will want to check the integrity of candidates. Integrity testing becomes even more essential in jobs where the employees handle a lot of sensitive information.
- Work Sample Testing – Work sample testing means the candidates are actually asked to perform the jobs that they be performing if selected. Based on their performance in those demonstrative samples, the actual expertise of the candidate can be evaluated. For example, asking potential drivers to take a driving test.
- Drug Testing – Finally some companies have a policy not to recruit anyone with a history of drug abuse or addition. So they may put the candidates through narcotic testing to rule out any such occurrences in the past.
Interviewing – Interviewing is the most frequently used method in selection. This process gives both the selector and the candidate to better understand each other and ask questions that will be important to the either side to arrive at a final decision. Different types of interviews are as follows;
- Structured Interviews
- Situational Interviews
- Behavioral Interviews
- Unstructured Interviews
Commonly Occurring Interview Errors
- Snap Judgements
- Negative Emphasis
- Halo & Horn Effects
- Biases
- Cultural Noise
Background Check – Reference check also known as background check is a step that verifies candidate’s personal as well as professional background. This is done to ensure that the candidate does not have an adverse historical event that may impact his performance in the organization or the organizational performance itself. Various methods used in this step are;
- Previous employers
- Professional Agencies
- Social Media Profiles
- Criminal Records
Medical Examination – Mostly all organizations, just before making a job offer to a candidate would like a medical test to be performed on the candidate by their designated healthcare provider. The purpose of this test to ensure that the candidate;
- Is free from any serious illness that may impact his performance.
- Does not have any health condition that prevents him from carrying out certain types of jobs.
- Does have any contagious disease that may jeopardize the health of other employees.
- Is not suffering not from any life-threatening illness that may cause immediate financial loss to the organization in terms of compensations to be paid in the event of his demise.
Related – Job Analysis, Job Design & Human Resources Planning
Induction
Induction is a critical component of recruitment, selection and induction trio. An induction program is the process used within many businesses to welcome new employees to the company and prepare them for their new role. Induction training should include development of theoretical and practical skills, but also meet interaction needs that exist among the new employees.
Steps In Induction
Depending the levels of candidates recruited and the requirement of special skills, induction programs vary greatly from role to role and company to company. some of the commonly witnessed steps in induction process are mentioned below;
- General Orientation – Carried out by the HR department. Involves introductions, showing around and completing the post joining formalities.
- Specific Orientation – Carried out by the functional department where the job posting has happened. Typically involves familiarization, training and handing over. This may last longer for fresher hires.
- Follow-up Orientation – Again conducted by the HR department after a predetermined time to assess the settling down of the employee and to fine tune any homogenization issues.
Benefits of Induction
Induction as the name suggest is an onboarding process that helps the employee settle down well in the new organization. On the other hand, it ensures faster availability of fully functional new employee. Some of the general benefits of induction are summarized as below;
For Employers
- Quicker Employee Productivity – Induction ensures faster settling down for the employee and quicker availability to his line function.
- Reduces Employee Turnover – Induction makes the onboarding process smoother and there are lesser chances of early attrition due acclimatization issues.
- Operational Efficiency – Induction program ensures that the new employees join their department fully informed and sorted. this results in higher productivity levels.
- Lesser Disputes – since the new employees are given detailed instruction about the organizational behavior, its culture and dos and don’ts, there are less chances of any disputes when the employee reaches his shop floor.
Additional Reading – Compensation Management | Key to Organizational Productivity and Success
For Employees
- Settling Down Comfortably – New employees get an opportunity to be introduced to their peers, supervisors and other members of the team. They are also imparted information about various forums and points of contact in case of any requirement. This ensure that the new employees settle down more comfortably.
- Establishing Communication – Initial introductions help in establishing good communications for the newcomers. This helps in keeping the new employees well engaged with the overall ecosystem of the organization.
- Motivating – The way the new employee is welcomed and imbibed into the organization influences the motivation level of the incumbent. The induction program should become a pleasant experience for the new comer!!
“Bet On People, Not On Strategies” – Lawrence Bossidy, retired CEO of AlliedSignal









