Environmental Appraisal – A Precursor To Strategy

Imagine you have to reach a destination by car. Before you get behind the wheel, don’t you subconsciously consider the following factors while planning your drive? Factors like time of the day or night, traffic conditions, condition of the road, condition of your car and your driving skills. Accordingly you calculate the amount of time and any extra resources you will require to reach your destination. You may also want to be prepared and take necessary precautions on the way. This is is called Environmental Appraisal. We do it all the time in our day to day lives but never realize it. It happens at the subconscious level without us even bothering to think about it. Same thing is done the business world, albeit consciously, in order to formulate and execute strategies and remain relevant in the business.
Environmental Analysis
Study of the environmental factors, both within an organization and outside, and their impact on the functioning of the organization is called the Environmental Analysis. Findings from the environmental analysis are used as input for formulating and implementing business strategies. In order to understand the environmental analysis, let’s first understand business environment and its components in more detail;
Related – Introduction To Strategic Management
Business Environment
Business environment is a mixture of complex, dynamic and uncontrollable external as well as internal factors within which a business is to be operated. Components of Business Environments are as follows;
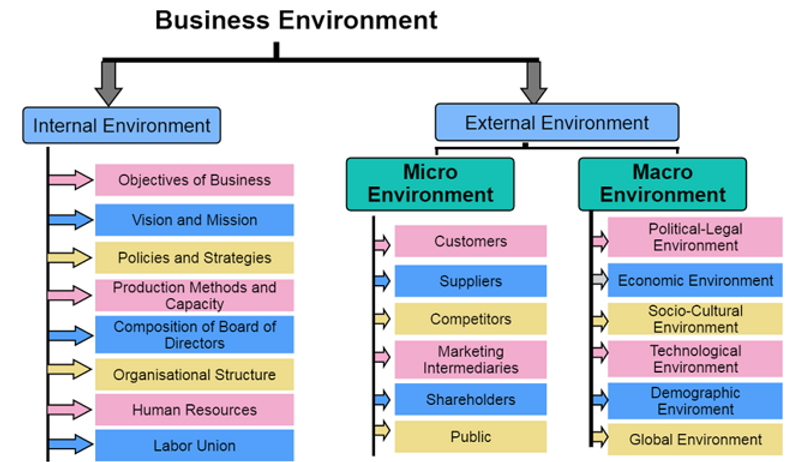
Internal Environment
Those factors which are within an organization and influence only the organization in question, together constitute the internal environment. Various factors that form the internal business environment are;
- Vision And Mission – Vision is the ultimate destination or the dream that the promoters visualize for the organization. On the other hand, mission is the reason for the existence of the organization and defines the course of action it will take.
- Objectives – Objectives are the milestones which are very specific and time bound. They are the starting point of a strategy. Objectives are supposed to be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Time Bound (SMART).
- Policies – Policies of an organization are the framework within which all the activities have to be planned and executed.
- Production Methods & Capacity – Production methods and capacity determine the qualitative and the quantitative capabilities of an organization. They are important to be considered while formulating strategies in order to achieve objectives such as market share, sales revenue, new product development etc.
- Organizational Structure – Organizational structure can have a lasting impact on the objectives and strategies. A flat organization compared to a vertically oriented, hierarchical organization has better availability of ideas and the chances of it succeeding will be more. However this is also largely dependent on the sector and the type of the organization.
- Human Resources – The number of employees and their skill levels as well as their motivation levels influence the objectives and the strategies formulation and implementation.
- Labor Union – The approach of the labor union in terms of whether it is hostile or cooperative will directly impact the functioning of an organization.
External Environment
Those factors or forces that exist outside the organization and influence not only the organization in question but the overall business scenario and the society. External environmental factors can be further classified into Micro Environmental Factors and Macro Environmental Factors.
Micro Environment – it is the immediate external environment surrounding an organization. The factors in the micro environmental factors influence the organization and the organization also to some extent exerts influence on these factors. Various components of the microenvironmental factors are summarized as below
- Customers
- Suppliers
- Computers
- Marketing Intermediaries
- Shareholders
- Community
Macro Environment – The larger environment of a region or a country in which all the businesses thrive and function is called the macro environment. The factors of the macro environment are such that they can influence any business operating within itself, but businesses can seldom influence these factors. Major components of the macro environment are listed and described as below.
- Political Environment
- Legal Environment
- Economic Environment
- Socio Cultural Environment
- Technological Environment
- Demographic Environment
- Global Environment
Nature Of Business Environment
It is important to understand the nature and behavior of the business environment in order to utilize the information. In formulating and executing our strategies, the factors that clearly specify the nature of business environment are as follows.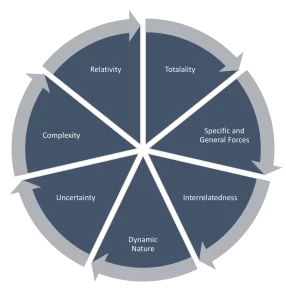
- The Totality Of External Forces – Business environment includes everything which is outside the organization. If we add all these forces, they will form a business environment.
- Specific And General Forces – There are some general forces like the environment, weather conditions, government policies, and then there are some specific forces like. Certain government policies impacting only a certain type of businesses.
- Interrelatedness – Most of the. Macro environmental factors are related to each other, for example. The tax structure. Off a particular. Economy is closely related to the political. Environment of the. Area.
- Dynamic Nature – The business environment and its factors. Our dynamic in nature in the sense that they keep changing and their influence on an organization also has different outcomes.
- Uncertainty – There is a lot of uncertainty with respect to the environmental influence. Environmental factors change. Fast and frequently, for example earthquakes or volcanic eruptions, can have a profound impact on all the businesses worldwide and they are absolutely uncertain and impossible to predict.
- Complexity – business environment is complex and its factors are intertwined. Sometimes the impact of one environmental factor is not directly felt and it is felt in the form of another factor imposing its influence on the business.
- Relativity – environ mental factors are highly relative. In the in nature, in the sense that they may show their adverse or positive impact on some business and. Equally opposite impact on another business.
Significance of Business Environment
Let us study. The significance of business environment. In successfully conducting our business and formulating and executing strategies.
- Helps in identifying opportunities and making first mover advantage
- Enables the firm to identify threats and early warning signals
- Helps in tapping useful resources
- Prepare the business for coping with rapid changes
- Assists in planning and policy formulations
- Helps in improving performance
Models of Environmental Analysis
Amongst the many tools that are available today, the following are the most widely used methods of environmental analysis.
VRIO Framework
Also known as Resource Based View, VRIO framework evaluates the available resources and the firm’s’ capability to leverage them to create a long term sustainable competitive advantage. The components of VRIO Analysis are:
- Value
- Rarity
- Imitability
- Organization

If a firm has resources that are valuable, rare, costly to imitate, and the firm is organized to exploit those resources, then the firm is aligned to enjoy a long-term sustainable competitive advantage.
Porter’s Five Forces Model
Porter’s Five Forces is a business analysis model that helps to explain why various industries are able to sustain different levels of profitability. Porter identified five undeniable forces that play a part in shaping every market and industry in the world.
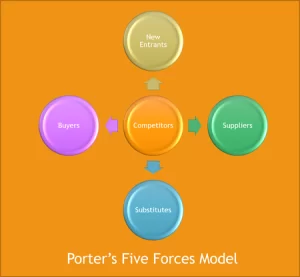
The five forces are frequently used to measure competition intensity, attractiveness, and profitability of an industry or market.
- Intra Category Rivalry
- Threat Of New Entrants
- Threat Of Substitutes
- Bargaining Power Of Customers
- Bargaining Power Of Suppliers
SWOT Analysis
A scan of the internal and external environment is an important part of the strategic planning process. Environmental factors internal to the firm usually can be classified as strengths (S) or weaknesses (W), and those external to the firm can be classified as opportunities (O) or threats (T). Such an analysis of the strategic environment is referred to as a SWOT analysis. The SWOT analysis provides information that is helpful in matching the firm’s resources and capabilities to the competitive environment in which it operates. As such, it is instrumental in strategy formulation and selection. The following diagram shows how a SWOT analysis fits into an environmental scan:
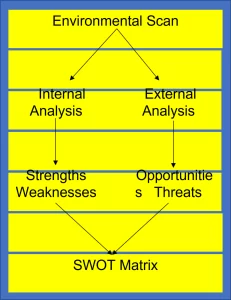
Strengths – A firm’s strengths are its resources and capabilities that can be used as a basis for developing a competitive advantage. Examples of such strengths include:
- Patents
- Strong brand names
- Good reputation among customers
- Cost advantages from proprietary know-how
- Exclusive access to high grade natural resources
- Favorable access to distribution networks
Weaknesses – The absence of certain strengths may be viewed as a weakness. For example, each of the following may be considered weaknesses:
- Lack of patent protection
- A weak brand name
- Poor reputation among customers
- High-cost structure
- Lack of access to the best natural resources
- Lack of access to key distribution channels
In some cases, a weakness may be the flip side of a strength. Take the case in which a firm has a large amount of manufacturing capacity. While this capacity may be considered a strength that competitors do not share, it also may be a considered a weakness if the large investment in manufacturing capacity prevents the firm from reacting quickly to changes in the strategic environment.
Opportunities – The external environmental analysis may reveal certain new opportunities for profit and growth. Some examples of such opportunities include:
- An unfulfilled customer need
- Arrival of new technologies
- Loosening of regulations
- Removal of international trade barriers
Threats – Changes in the external environmental also may present threats to the firm. Some examples of such threats include:
- Shifts in consumer tastes away from the firm’s products
- Emergence of substitute products
- New regulations
- Increased trade barriers
The SWOT Matrix
A firm should not necessarily pursue the more lucrative opportunities. Rather, it may have a better chance at developing a competitive advantage by identifying a fit between the firm’s strengths and upcoming opportunities.
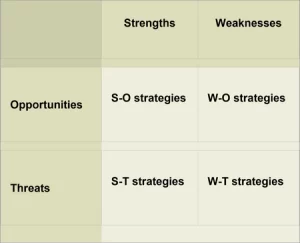
In some cases, the firm can overcome a weakness in order to prepare itself to pursue a compelling opportunity. To develop strategies that consider the SWOT profile, a matrix of these factors can be constructed. The SWOT matrix (also known as a TOWS Matrix)
• S-O strategies pursue opportunities that are a good fit to the company’s strengths.
• W-O strategies overcome weaknesses to pursue opportunities.
• S-T strategies identify ways that the firm can use its strengths to reduce its vulnerability to external threats.
• W-T strategies establish a defensive plan to prevent the firm’s weaknesses from making it highly susceptible to external threats.
PESTEL Analysis
A PESTEL analysis incorporating political, economical, social, technological, legal and environmental factors is called a PESTLE analysis.
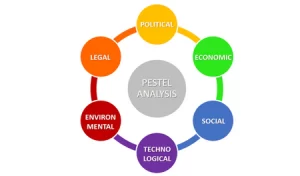
Political – The first element of a PEST analysis is a study of political factors. Political factors influence organizations in many ways. Political factors can create advantages and opportunities for organizations. Conversely, they can place obligations and duties on organizations. Political factors include the following types of instruments:
- Legislations such as minimum wages or anti-discrimination laws.
- Business Regulators
- Trade agreements, tariffs or restrictions
- Tax levies and Tax breaks
- Type of government regimes, e.g., communist, democratic, dictatorship.
- Anti-competitive practices prevention
Non conformance with legislative obligations can lead to sanctions such as fines, adverse publicity and imprisonment. Ineffective voluntary codes and practices will often lead to governments introducing legislation to regulate the activities covered by the codes and practices.
Economic
- Purchasing Power
- Labor Costs
- Type of Products
- Spending Patterns of well-to-do customers
- Currency Fluctuations
- Interest Rates
Social
- Time-Poor Society
- Children’s Influence on Buying
- Privacy Concerns
- Greener Customers
Technology
- New Products – Competition
- New Channels of Communication
- New Channels of Distribution
Legal
- Labor Laws
- Quality Monitoring Laws
- Voluntary Disclosures
Environmental
- Power Consumption
- Recycling
- Pollution Norms
- Affluent Discharge
- Carbon Footprint







